
Secondary peritonitis chest x ray wikidoc
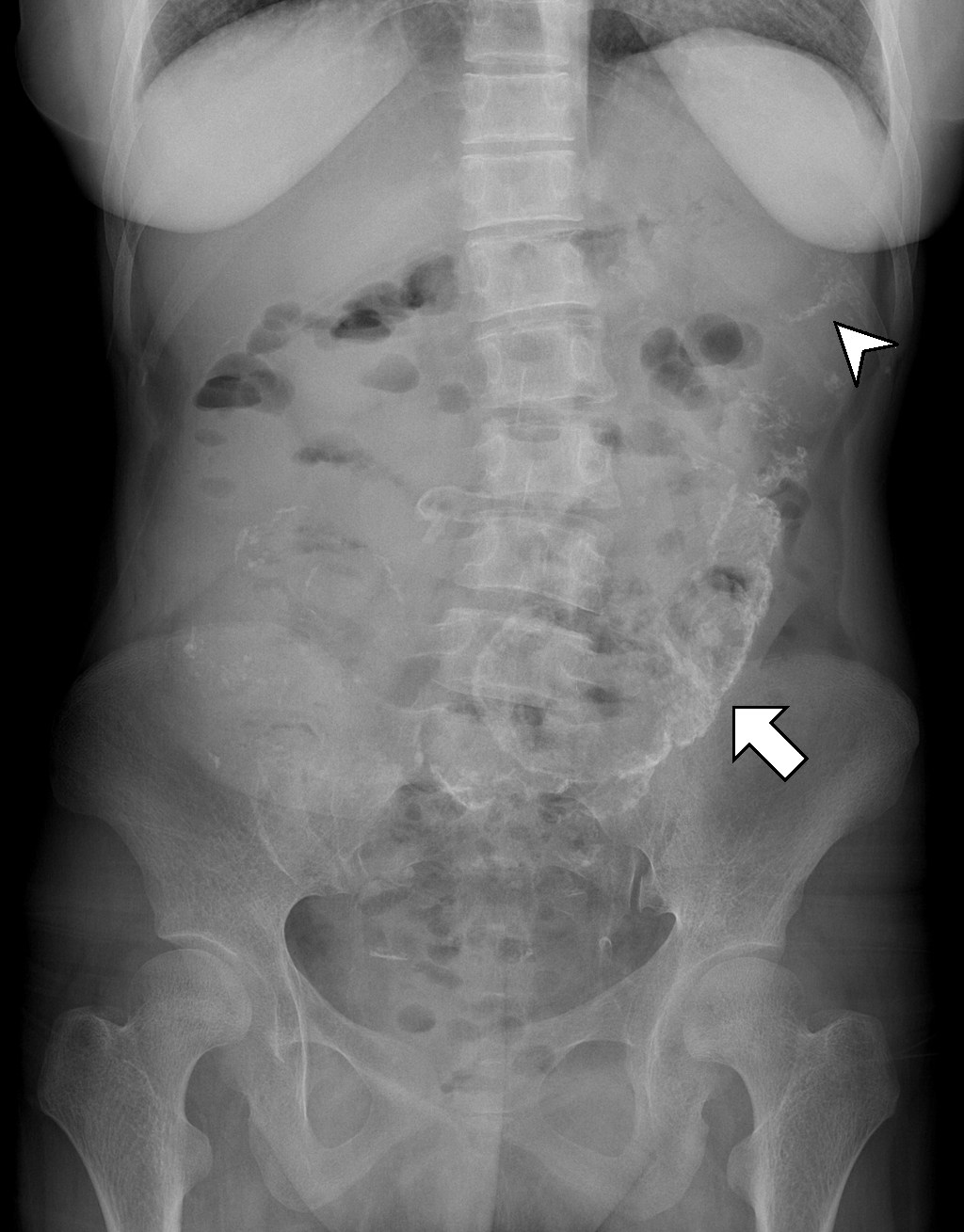
Age: 5 years Gender: Female ct Multiple loculated peritoneal collections with a thick enhancing wall, most of which show gas fluid levels, some of the collections are interconnecting. Largest loculated collection in the recto-uterine pouch measures 5 x 5 x 3.7 cm. A small subcapsular hepatic collection is also noted.

Meconium peritonitis Radiology Case
Age: 17 years Gender: Male ct Axial C+ arterial phase Coronal C+ portal venous phase Sagittal C+ portal venous phase Axial C+ delayed MDCT reveals a large amount of high density fluid in the peritoneal cavity associated with diffuse thickening of peritoneal lining. There is no evidence of free air or leak of oral contrast material.
EPOS™ C2408
CT findings of peritonitis likely tuberculous (the tumor marker results were negative), however the histopathological/laboratory assessment of the fluid aspirate, omental biopsy (preferably ultrasound guided), and culture are required to confirm the presence of caseating granulomas and AFB before commencing treatment.

Sclerosing encapsulated peritonitis typical imaging findings for easy
The clinical diagnosis of peritonitis is based on acute abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness and guarding, fever, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and bloating; laboratory data such as leukocytosis and acidosis are supportive. Go to: Normal vs. pathologic peritoneum: CT appearance

Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis The Abdominal Cocoon RadioGraphics
Definitions • Infectious or inflammatory process involving peritoneum or peritoneal cavity IMAGING General Features • Best diagnostic clue Ascites and omental/mesenteric fat stranding with symmetric, smooth enhancement and thickening of peritoneal lining • Location Peritoneal surface, mesentery, and omentum • Size

Pneumoperitoneum Image
causes Diagnosis & treatment Overview Peritonitis is a serious condition that starts in the abdomen. That's the area of the body between the chest and the pelvis. Peritonitis happens when the thin layer of tissue inside the abdomen becomes inflamed. The tissue layer is called the peritoneum.
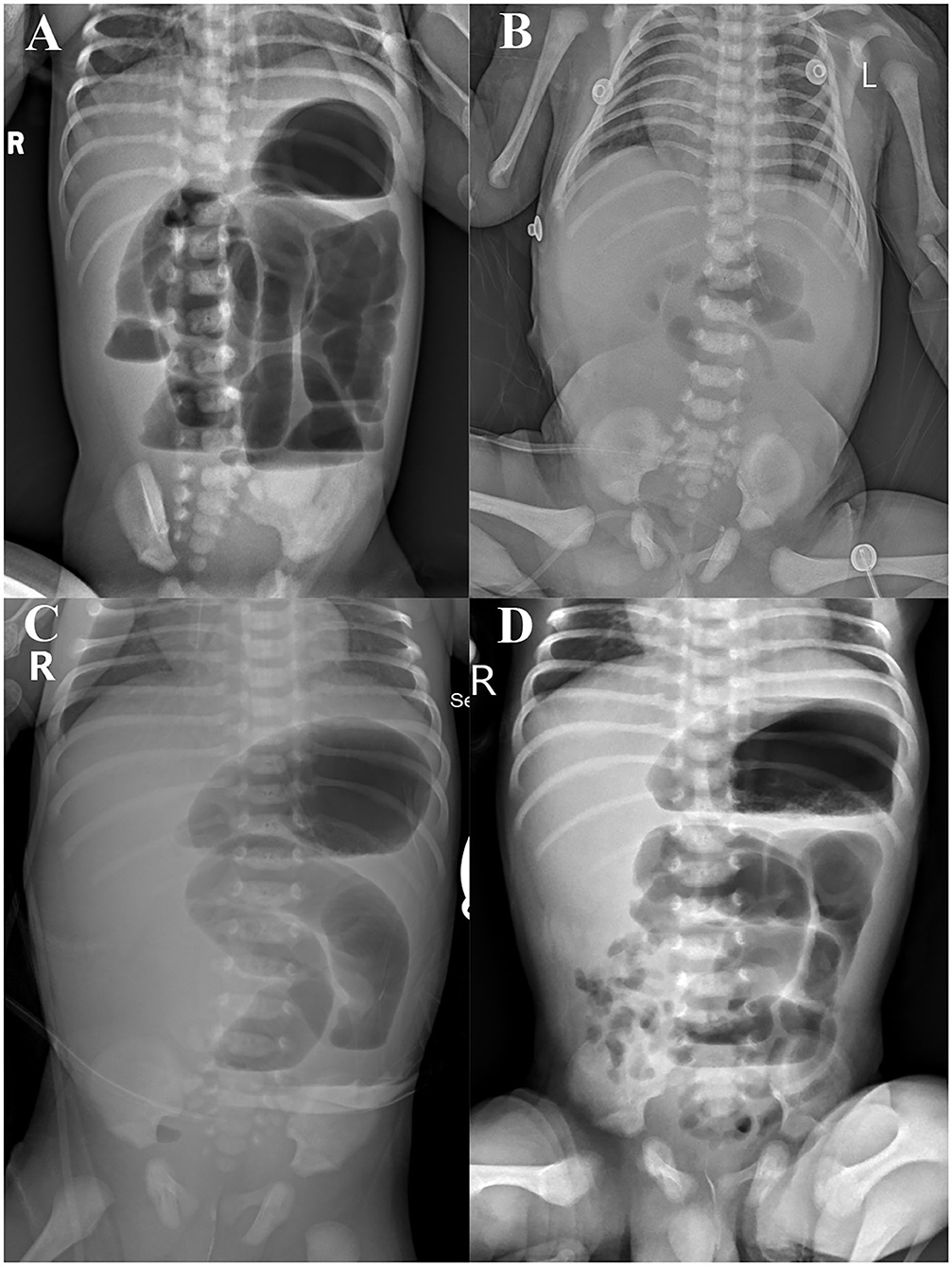
Frontiers Meconium Peritonitis, Intestinal Atresia Combined With
Finally, imaging studies, such as X-rays or CT scans, can show perforation or other trauma in the gastrointestinal tract. If peritonitis is associated with peritoneal dialysis, a physical exam assessing signs and symptoms may be enough to diagnose the condition. In particular, cloudy dialysis fluid is highly indicative of peritonitis.
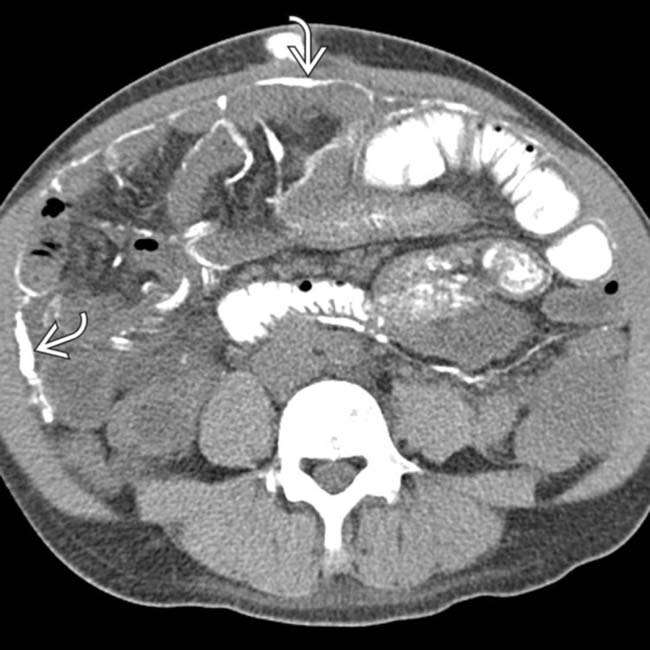
Peritonitis Radiology Key
Peritonitis is a redness and swelling (inflammation) of the tissue that lines your belly or abdomen. This tissue is called the peritoneum. It can be a serious, deadly disease. What causes peritonitis? Peritonitis is caused by an infection. Bacteria can enter the lining of your belly from a hole in your GI (gastrointestinal) tract.

Image
treatment Diagnosis To diagnose peritonitis, your health care provider talks with you about your medical history and gives you a physical exam. Your symptoms alone may be enough for your provider to diagnose the condition if your peritonitis is linked to peritoneal dialysis.
Neonate, perforation with meconium peritonitis radRounds Radiology
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. [2] Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. [2] [3] One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. [1]

Secondary peritonitis chest x ray wikidoc
Primary peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum by an extraperitoneal source, frequently occurring from hematogen dissemination. It occurs in children and adults and can endanger life, particularly in patients who have cirrhosis or in children who have nephrosis.

Secondary peritonitis CT wikidoc
Peritonitis, an inflammation of the peritoneum, is a life-threatening acute surgical emergency. It presents with severe abdominal pain and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality ranging from 10%-60% in surgical settings [ 1 ].
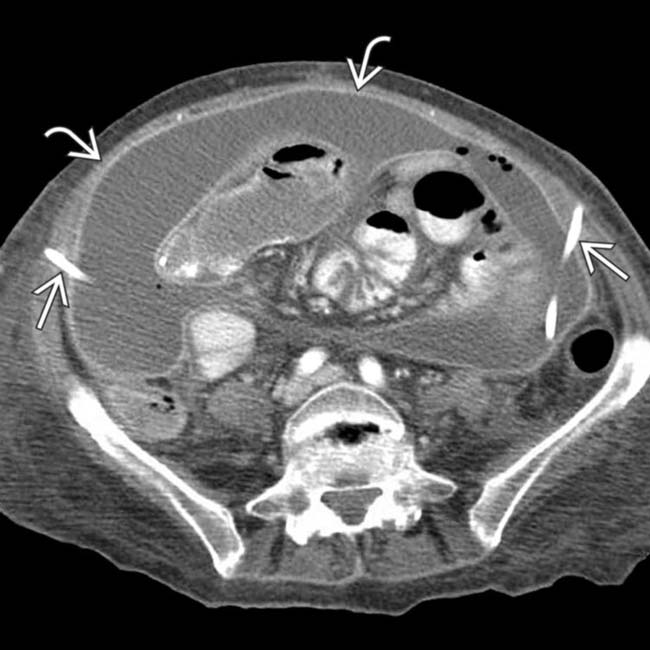
Peritonitis Radiology Key
Peritonitis is the reaction of the peritoneum against bacterial contamination or intrinsic chemical toxins in the abdominal cavity. This response is initially characterized by congestion and increased secretion of fluid and macrophages into the peritoneal cavity.

PERFORATION HOW TO SPOT FREE INTRAPERITONEAL AIR ON ABDOMINAL
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Peritoneal pathology essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Peritoneal pathology: Peritonitis. Pneumoperitoneum.

Peritonitis Image
anorexia, or loss of appetite excessive thirst fatigue fever and chills If you're on peritoneal dialysis, your dialysis fluid may appear cloudy or have white flecks or clumps in it. You may also.

Meconium peritonitis an interesting entity BMJ Case Reports
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is a potentially life-threatening complication of ascites diagnosed by paracentesis. We determined predictors of SBP to facilitate patient selection. The 301 paracenteses performed in 119 patients (51 women, 68 men) from July to November 2015 were retrospectively reviewed.